Consider adjuvant radiotherapy:
Can be offered as primary treatment for patients who are not suitable for surgery, as adjuvant or palliative treatment
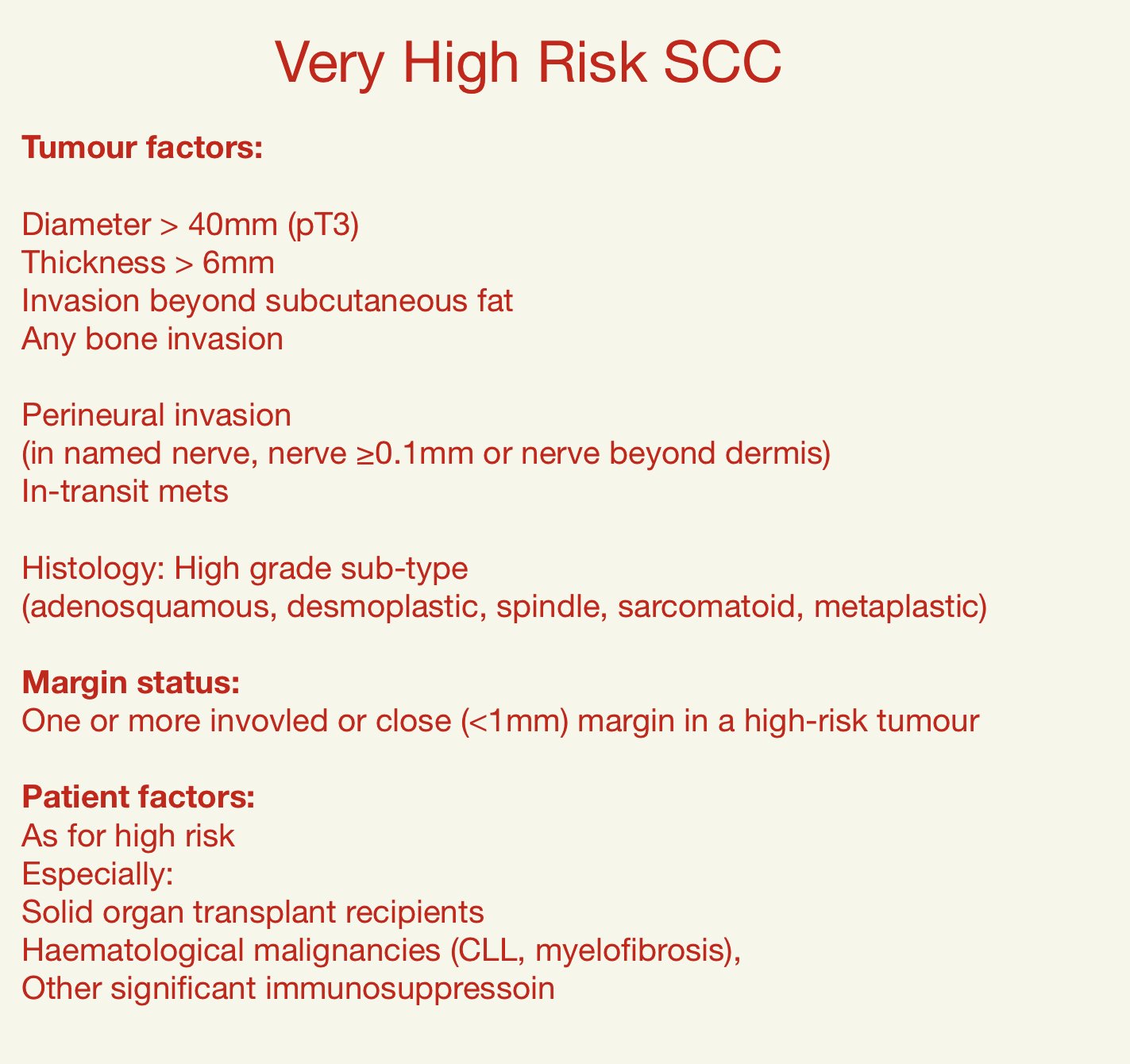
Main high risk pathological features for post-op radiotherapy:
pT3
Margins < 1mm
Thickness > 6mm4
Invasion beyond subcutaneous fat
Perineural invasion (multifocal, named nerve, nerve diameter > 0.1mm, below dermis)
Recurrent disease
Immunodeficiency
Guidelines:
BAD guidelines
NCCN guidelines
INTRODUCTION
Cutaneous SCC is the 2nd most common skin cancer
SCCs generally have a good prognosis with 5-year survival of about 98%
But they have the potential to produce substantial local destruction along with disfigurement
They may involve extensive areas of soft tissue, cartilage and bone
They can rarely metastasize
Risk factors:
Chronic and cumulative sun exposure
Sunbeds
Light skin, hair and eye colour
Tend to occur in sites of sun-exposed skin (especially head and neck)
May occur in scars or chronic wounds or sites of chronic inflammation
Genetic syndromes - albinism, xeroderma pigmentosa
Immunosuppression - organ transplant, lymphoma, CLL, HIV, Drug induced immunosuppression
(Of note organ transplant registries report a 5-fold to 113-fold increase in incidence of SCC compared to the general population)
BAD guidelines were published in 2020 for the management of cSCC
In addition to low-risk and high-risk groups they introduced a further very-high risk group
When dealing with assessing risk in cutaneous SCC need to think about patient factors, clinical characteristics and histological characteristics
MDT discussion is not required for low-risk T1 cSCCs with adequate histolgoical margins (>1mm clearnace) in the absence of other upstaging clinical risk factors (eg immunosupressioin)